|
 |
 |
 |
Allele frequencies:
allele frequency: the proportion of a certain allele within a population.
Fact: allele frequency = gene frequency = gametic frequency
gene pool: the set of all alleles at all loci in a population.
The Hardy-Weinberg genetic equilibrium:
no genetic drift (i. e. the population size is infinitely large)
no migration.
random mating
no selection.
The allele and genotypic frequencies remain the same from generation to generation in a population in which there is
no mutation
Moreover, the equilibrium genotype frequencies are given by
p2: the frequency of the homozygous dominant genotype
2pq: the frequency of the heterozygous genotype
q2: the frequency of the recessive genotype.
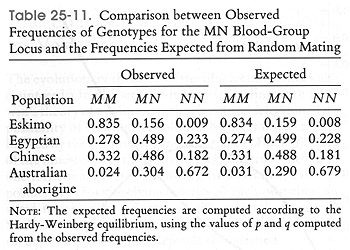
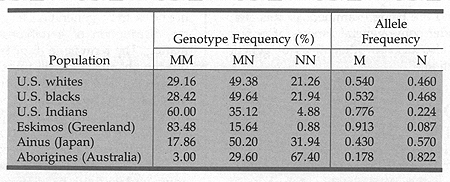
Frequencies for some alleles can be very close to the equilibrium
values, such as in the case of the MN alleles in humans.
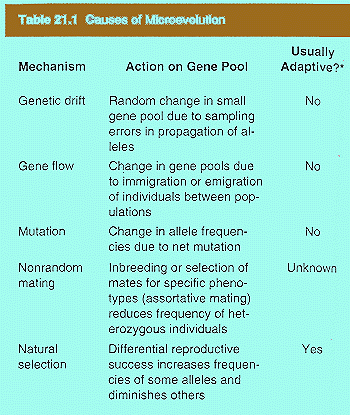
Processes Causing Deviations from the Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
1. Mutation
2. Genetic Drift
3. Migration
4. Nonrandom Mating
5. Selection
evolution: changes in allele frequencies in a population.