4. Nonrandon Mating
Inbreeding: mating between relatives.
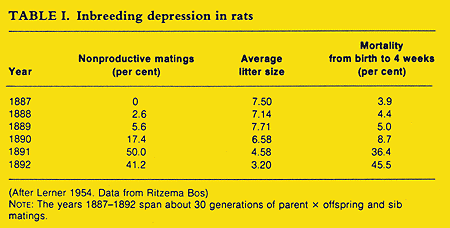
inbreeding depression: decrease of vigor or reproductive success due to inbreeding.


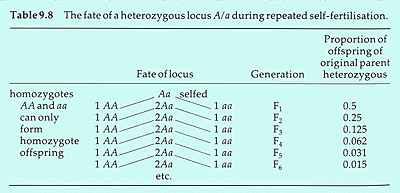
Fact: During selfing, the most extreme form of inbreeding, heterozygosity is halved between generations.
Fact: Positive assortative mating increases homozygosity only at the locus for which the choice occurs.
Fact: Asexual reproduction results in offspring that are genetically identical to the parent.

Hybrids are often superior in performance to more homozygous strains, as demonstrated in corn.